
Back بانثينول Arabic دکسپانتنول AZB Pantenol BS Panthenol German Pantenol Spanish دکسپانتنول Persian Pantenoli Finnish Panthénol French 판테놀 Korean Пантенол Macedonian
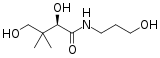 D-panthenol
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4-Dihydroxy-N-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutanamide[1] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1724945, 1724947 R | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.839 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | dexpanthenol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H19NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 205.254 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Highly viscous, colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.2 g mL−1 (at 20 °C) |
| Melting point | 66 to 69 °C (151 to 156 °F; 339 to 342 K) [contradictory] |
| Boiling point | 118 to 120 °C (244 to 248 °F; 391 to 393 K) at 2.7 Pa |
| log P | −0.989 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.033 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 0.964 |
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
+29° to +30° |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.499 |
| Pharmacology | |
| A11HA30 (WHO) D03AX03 (WHO), S01XA12 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
10,100 mg kg−1 (intraperitoneal, mouse); 15,000 mg kg−1 (oral, mouse) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Panthenol (also called pantothenol) is the alcohol analog of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), and is thus a provitamin of B5. In organisms, it is quickly oxidized to pantothenic acid. It is a viscous transparent liquid at room temperature. Panthenol is used in pharmaceutical and children's products as a moisturizer and to hasten wound healing.
- ^ "Dexpanthenol – Compound summary". PubChem Compound. US: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 25 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 29 June 2012.
